(see also: Therapeutic Principles & Anti-Gout Meds
Discussion
- gout refers to articular dz of MSU deposits (tophi) in soft tissues.
- it is caused by deposition of monosodium urate crystals in poorly perfused tissues, as well as bursae, ligaments, articular cartilage, and synovial membranes;
- on average, a family history of gout can be obtained in less than half patients'
- male / female ratio ranging from 7:1 to 9:1
- females with gout tend to be postmenopausal;
- pathophysiology
- predisposing conditions:
- common chronic diseases assoc w/ gout include alcoholism, obesity, hypertension, CAD, and hypertriglyceridemia;
- one beer a day may increase the uric acid level by 0.4 mg/dL and cause 50% increase in incident gout;
- increased dietary purine intake;
- decreased puring biosynthesis (lack of serum enzyme uricase);
- medications: thiazide diuretics and antimetabolites
- conditions which increase purine biosynthesis
- myeloroliferative disorders (polycythemia, AGL, CGL)
- multiple myeloma;
- sickle cell;
- prolonged use of diuretics (thiazide diuretics may precipitate gout);
- references:
- diff dx:
- prognosis:
- arthritis remits completely and then recurs with increasing frequency;
- in a pt w/ h/o acute gout, there is an 86% occurance of recurrent acute attack 3-5 days postoperatively if no prophylaxis is used;
- after 1st attack, 2/3 of these pts will develop 2nd attack w/in 1 year;
- w/in 2 years, three fourths will suffer a second attack;
- 1/10 of these pts will not have 2nd attack for following 10 years;
- w/ chronic gout, tophi develop in cartilage, tendons, and bursae in some patients
Clinical Presentation
- age: attacks of gout usually begin in males between ages of 30 and 50;
- when women are affected they are usually post-menopausal (and are not on supplemental estrogen);
- gout in women should prompt a more detailed work up of enzyme deficiency;
- patients may complain of very mild attacks developing w/o provocation that abate w/o specific treatment;
- podagara:
- classic presentation of acute attack of first MTP joint;
- hand:
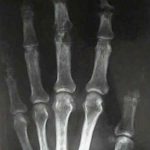
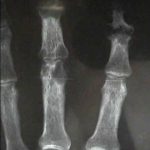
- may be confused with a hand infection;
- may present with synovial swelling, joint swelling, tenosynovitis;
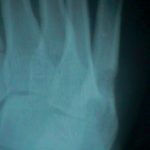
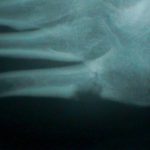
- in the hand look for oval periarticular erosions;
- multiple erosions will be distributed throughout the carpi and phalanges bilaterally;
- erosions have sclerotic borders and will often have overhanging edges;
- unlike classic RA, in early gout, hand and wrist joints will have preserved joint spaces and normal mineralization;
- nephrolithiasis is major extraarticular manifestation;
- in the urinary tract, the pH is less than 5.7, which causes urate to form of uric acid, which has poor solubility can cause precipitation of uric acid crystals;
- only small % of pts w/ gout get tophi, but many get renal stones;
- pure uric acid stones are found in 80%, & uric acid is probably nidus for Ca-Phos & oxalate calculi in remainder;
- in 1/2, sx from renal stones actually precede arthritis.
Laboratory Studies for Gout »
Radiographs
- in the hand look for oval periarticular erosions;
- multiple erosions will be distributed throughout the carpi and phalanges bilaterally;
- erosions have sclerotic borders and will often have overhanging edges;
- unlike classic RA, in early gout, hand and wrist joints will have preserved joint spaces and normal mineralization;
- example:
- case of histologically proven gout involving the proximal 5th metatarsal: