- Assymmetrical osteopenia;
- Spine: vertebral compression fractures;
- Skull:
- so-called salt-and-pepper skull
- tiny punched out lesions may be present in the skull, producing so called salt and pepper appearance;
- Clavicle: erosion of the outer centimeter of the clavicle
- Tibia: marked osteopenia of the medial aspect of the tibia
- Phalanges:
- subperiosteal resorption of digital tufts and phalanges (which is usually more marked on radial than on
ulnar side of the hand);
- look for resorption of phalangeal tufts and replacement of usually sharp cortical outline of bone in digits
by irregular outline (subperiosteal resorption);
- ref: Images in Clinical Medicine. Subperiosteal Bone Resorption
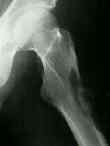
- Brown Tumors:
- occurs in severe cases;
- referred to as "Giant Cell Tumor of Diaphysis"
- microscopical exam revealed that it was composed of numerous osteoclasts with stromal hemorrhage;
- ref: A case of multiple skeletal lesions of brown tumors, mimicking carcinoma metastases
- Soft Tissues Calcification: (see: diff dx)
- occurs due to increase in serum calcium & serum phosphate (seen in secondary HPT);
- special sites of affinity for calcification include triangular ligament in the distal radio-ulnar articulation, menisci, and
articular cartilages;
- chondrocalcinosis can be seen by itself in elderly and has been associated with chronic disorders such as osteoarthritis,
rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, and Paget's disease;
- Bone:
- mobilizes bone and phosphate;
- releases osteocytic perilacunaar stores (fast)
- increases osteocytic number and activity (slow)
- activating and increasing number of osteoclasts, which destroys hydroxyapatite, thus releasing calcium and phosphate

