(see also: Spondyloarthropathies)
Discussion
- affects young men (ages 15 to 25 years), but may also begin in middle-aged men;
- disease is often more severe when it occurs early in life;
- disease characterized by insidious onset of pain and stiffness in lower back associated w/ gradual loss of spinal mobility;
- illness may cause inflammation in uveal tract (iritis in 25%) & in intima of aorta;
- symptoms are typically worse in the morning and in the middle of the night;
- note: that in women, the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis often first present during pregnancy;
- labs: HLA-B27 (may be present in up to 8% of unaffected white population);
- may also be present in Reiter's syndrome;
Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis »
- disorder has a tendency to progress slowly, w/ diminished mobility of the spine and sacroiliac joints;
- early diagnosis can often be made with a CT scan of the sacroiliac joints;
- cervical spine in ankylosing spondylitis:
- acute neck pain in pt w/ AS is usually caused by frx thru ankylosed spine;
- frx involves all columns & may be assoc w/ dramatic change in neck alignment;
reference: Uncommon Complication After Revision Hip Surgery
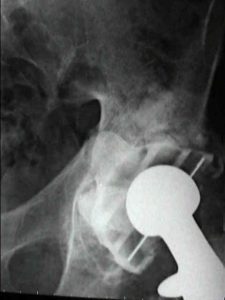 Peripheral Arthritis
Peripheral Arthritis
- may involve hips, knees, ankles, toes, (rare upper extremities).
- these may precede the back pain by several years;
- arthritis is acutely painful but rarely chronic or destructive;
hip joint
- is affected in up to 50 % of patients with AS, and when it occurs it is often bilateral;
- protrusio and hip flexion contractures are common;
- heterotopic ossification may follow THR;
- total hip replacement:
- hetertopic ossification of the hip;
- occurs in 20-40 % of hip replacements and is more common w/ trochanteric osteotomy;
- to avoid heterotopic ossification consider insertion of a cemented acetabular component followed by 750 rads around the component;
- hetertopic ossification of the hip;
Childhood AS
- AS may develop in children & resembles pauciarticular JRA;
- usually boys over 8 years of age
- asymmetric peripheral arthritis of lower extremities.
- must be differentiated from DISH;
Management
- NSAIDS: patients should be placed on indocin as soon as the diagnosis is made;
- tumor necrosis factor inhibitors:
- sulfasalazine:
- may attenuate the inflammatory exacerbations;
- effect starts within the first 2 to 3 months;
- dose can be gradually decreased after 6 months, and then slowly stopped;
- begin with full dose (2 g/day) or start with 500 mg/day weekly increasing the dose to 1 g/bid;
- dose can be increased up to 3 g/day;
- less effective in chronic cases
- may attenuate the inflammatory exacerbations;
References
- Disorders of the sacro-iliac joint in children.
- Total hip replacement for patients who have ankylosing spondylitis. The importance of the formation of heterotopic bone and of the durability of fixation of cemented components.
- The Shoulder Girdle in Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Ankylosing spondylitis: experience in surgical management of 21 patients
- The clinical spectrum of ankylosing spondylitis.
- Long term results of total hip replacement in young patients who had ankylosing spondylitis. Eighteen to thirty-year results with survivorship analysis.

