- Technique:
- prepare the patient as for subclavian approach;
- right side of the neck is preferred for venipuncture for three reasons:
- dome of the right lung and pleura is lower than left;
- there is more or less a straight line to the atrium;
- the large thoracic duct is not endangered;
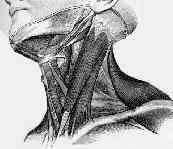
- locate the triangle formed by the clavicle and the two heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle;
- internal jugular vein runs deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and then through this triangle before it enters into the subclavian vein;
- patient is placed in Trendelenburg's position with the head rotated 45 degrees away from the insertion site;
- strict sterile technique;
- use a 25 gauge needle and 1% lidocaine to raise a small skin wheal in the center of this triangle;
- finder needle:
- use one hand to palpate the carotid artery;
- 22 gauge needle to anesthetize the deeper layers, and then use gentle aspiration, with the same needle, to initially locate internal jugular vein;
- needle is inserted immediately lateral to the carotid pulse and slightly superior to the apex of the triangle.
- needle is inserted past the apex of the triangle, towards the ipsilateral nipple, at an angle of 20 deg;
- vein is located near the skin surface and often is less than 1.5 cm from the skin surface;
- if the attempt is unsuccessful, then the needle is aimed more medially on the next insertion attempt;
- attach a thin walled 18 gauge cannula-over-needle or 16 gauge intracath needle to a 10-20 ml syringe;
- direct the needle thru the skin wheal caudally, directed toward the ipsilateral nipple and at a 30 deg angle to the frontal plane;
- if vein is not entered, withdraw the needle and slightly redirect it 10-15 degrees more laterally;
- apply constant back pressure;
- if bright red blood forcibly fills the syringe, you have punctured the carotid artery;
- remove the needle and apply firm pressure for 10 min;
- follow the proceedure for subclavian vein approach;
- Cautions:
- this approach is contraindicated with coagulopathy because pressure cannot be applied if expanding hematoma occurs
Prevention of Intravascular Catheter–Related Infections.
Central Venous Catheterization
Emergency War Surgery - vascular access
Ultrasound-Guided Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation
Anomalous external jugular vein: clinical concerns in treating clavicle fractures

