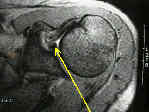
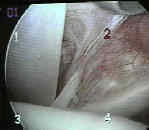
- See: shoulder joint menu and arthroscopic RCT repair
Fluid Management:
Positioning:
- beach chair position is comfortable for both the patient and the surgeon and allows the option of converting to an open procedure (if necessary);
- patients need to be seated with the torso raised to 70 deg with a foled sheet placed on the medial border of affected scapula (to maximize posterior exposure)
- complications: hypoglossal nerve injury;
References:
-
- Measurements of brachial plexus strain in arthroscopy of the shoulder.
- Hypoglossal nerve palsy after arthroscopy of the shoulder and open operation with the patient in the beach-chair position. A case report.
- Avoiding catastrophic complications of stroke and death related to shoulder surgery in the sitting position.
- Pathomechanisms and Complications Related to Patient Positioning and Anesthesia During Shoulder Arthroscopy
- A cardiovascular collapse occurred in beach chair position for shoulder arthroscopy under general anesthesia -A case report.
Portal Placement:
References:
- Glenohumeral arthroscopy portals established using an outside-in technique: neurovascular anatomy at risk.
- The low anterior five-o'clock portal during arthroscopic shoulder surgery performed in the beach-chair position
- Anatomic Risks of Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals: Anatomic Cadaveric Study of 12 Portals.
Arthroscopic Techniques:
- arthroscopic acromioplasty
- arthroscopic glenohumeral reconstruction
- slap lesions
- rotator cuff tears - management of massive rotator cuff tears
References
- Arthroscopy of the shoulder: technique and normal anatomy.
- What Adverse Events and Injuries Are Cited in Anesthesia Malpractice Claims for Nonspine Orthopaedic Surgery?
- Arthroscopic alphabet soup: recognition of normal, normal variants, and pathology
- “Put Your ‘Extended’ Finger on the Bleeder”: The Use of Direct Pressure From the Shaver Blade to Achieve Hemostasis