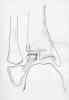
- Discussion:
- SH III frx involving avulsion of anterolateral tibial epiphysis;
- occurs in older adolescents, after the middle and medial parts of epiphyseal plate has closed, but before the lateral part closes (usually 12 to 15 yrs of age);
- because, this frx occurs in adolescents w/ relatively mature growth plates, there is minimal potential for deformity due to growth plate injury;
- Mechanism of Injury:
- external rotation force w/ stress placed on anterior tibiofibular ligament, causing avulsion of distal tibial epiphyseal plate anterolaterally;
- further lateral rotation causes displacement of fracture;
- frx occurs after medial part of the epiphyseal plate has closed, but before the lateral part closes;
- resultant frx thru epiphyseal plate runs across epiphysis and distally into the joint, creating SH type III or IV frx;
- Radiographs:
- AP and Oblique views are needed to distinguish from a triplane frx;
- note that the common triplane fracture will contain a tillaux fracture in addition to the tibial physeal frx;
- Non Operative Treatment:
- attempt closed reduction (internal rotation of ankle and supination of foot) but accept no displacement;
- the surgeon may perform direct pressure over the fragment inorder to effect the reduction;
- patients should initially be placed in a long leg cast;
- Operative Treatment:
- significantly displaced fragmentss require anatomic reduction & fixation to restore satisfactory function of the ankle joint;
- perform ORIF thru anterolateral approach using cancellous screws or K wires;
- incision begins over anterolateral aspect of the leg medial to the fibula and 1.5 inches proximal to the ankle joint;
- extensor tendons, dorsalis pedis artery, and deep peroneal nerve are retracted medially;
- ankle capsule is opened and the anterior tibiofibular lig is identified;
- frx of the anterolateral portion of tibial plafond is visualized;
- screw placement or pin placement is allowed to cross the physis since the physis is in the process of closing;
- consider using a K wire as a fixation joystick to help effect the reduction
Triplane and Tillaux Fractures: Is a 2 mm Residual Gap Acceptable?
Radiologic Evaluation of Juvenile Tillaux Fractures of the Distal Tibia
The juvenile fracture of Tillaux.
Fracture of the lateral portion of the distal tibial epiphysis.
Fractures of the distal tibial epiphysis in adolescence.
Juvenile Tillaux fracture simulating syndesmosis separation: a case report.

