- Discussion:
- most common;
- occur thru base of odontoid process & may be caused by either hyper-flexion or hyperextension forces;
- blood supply is often comprimised in a type 2 frx
- type II frx occurs at base of dens, typically, frx plane is transverse;
- when dens displacement occurs, the C-1-dens-transverse ligament complex usually remains intact;
- ligamentous disruption may involve thick atlantoaxial capsular lig;
- non union:
- non union occurs in 30-50%, esp in elderly w/ > 5mm of displacement;
- greater rate of nonunion occurrs in pts who had sig displacement (angulation > 10 degrees or translation > 5 mm) & are rxed
w/ halo device compared to rx w/ arthrodesis;
- in atlanto-axial instability persists, spinal cord compression and paralysis may result;
- risk factors for non union:
- comminution at the base of the odontoid (strong negative risk factor);
- older age
- initial displacement amount > 2 mm (and especially if more than 4 mm);
- initial displacement direction (posterior worse than anterior)
- residual posterior displacement is also associated w/ more pain than w/ anteiror displacement;
- delay in dx
- redislocation in halo;
- ref:
- Non Union of fractures of the atlas.
- Non Union of the odontoid process: An experimental investigation.
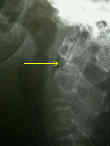
- Radiographs:
- prevertebral soft tissue swelling;
- dynamic flexion & extension views ;
- thin section CT w/ saggital reformations may be necessary;
- Non Operative Treatment:
- management w/ halo vest for 3 months is used if:
- initial dens displacement is < 5 mm;
- reduction is maintained,
- pt is younger than 50 years of age;
- 93% of pts heal solidly in halovest w/ the following conditions:
- age < 65
- anterior displacement less than 5 mm or posterior displacement less than 2 mm;
- diagnosis is made within one week;
- in the study by Stoney et al. 1998, management of these injuries with a halothoracic vest yielded a union rate of 82%;
- in the 18% of patients that failed to unite, there was no late neurological sequelae;
- risk factors for non union were extension type of injury, age over 65, and delay in dx;
- Operative Rx:
- posterior atlantoaxial arthrodesis with wire and bone graft has a 95% fusion rate, although an intact C-1 posterior arch is prerequisite;
- anterior screw fixation:
- in the study by Henry et al, 81 patients with odontoid fractures underwent anterior screw fixation.
- 29 patients had type II fractures and 52 patients had type III fractures;
- 92% of patients achieved bony union at an avg of 14 weeks;
- two patients required seceondary posterior fusion;
- full range of motion was restored in 43 patients;
- ref: Fixation of odontoid fractures by an anterior screw.
- Associated Frx:
- atlas frx: (see: Jefferenson frx)
- halovest until the C-1 arch is healed, then a posterior C-1 & C-2 arthrodesis if the dens has not healed
- because of this association, it is prudent to obtain a CT scan of the C-spine, in all patients w/ a dens frx, esp if
C1-C2 fusion is being considered;
- transverse ligament rupture:
- may occur in 10% of patients w/ type II dens fracture;
- MRI is used to make the diagnosis;
- non operative treatment would be expected to result in atlantoaxial instability;
- references:
- Transverse atlantal ligament disruption associated with odontoid fractures.
Management and Outcome of Dens Fracture Nonunions in Geriatric Patients
New subtype of acute odontoid fracture (type II A).
Treatment of type two odontoid fractures in halothoracic vests.