- See:
- arteries of the upper limb
- subclavian vein
- thoracic outlet syndrome;
- Discussion:
- injuries are rare because of overlying bony skeleton;
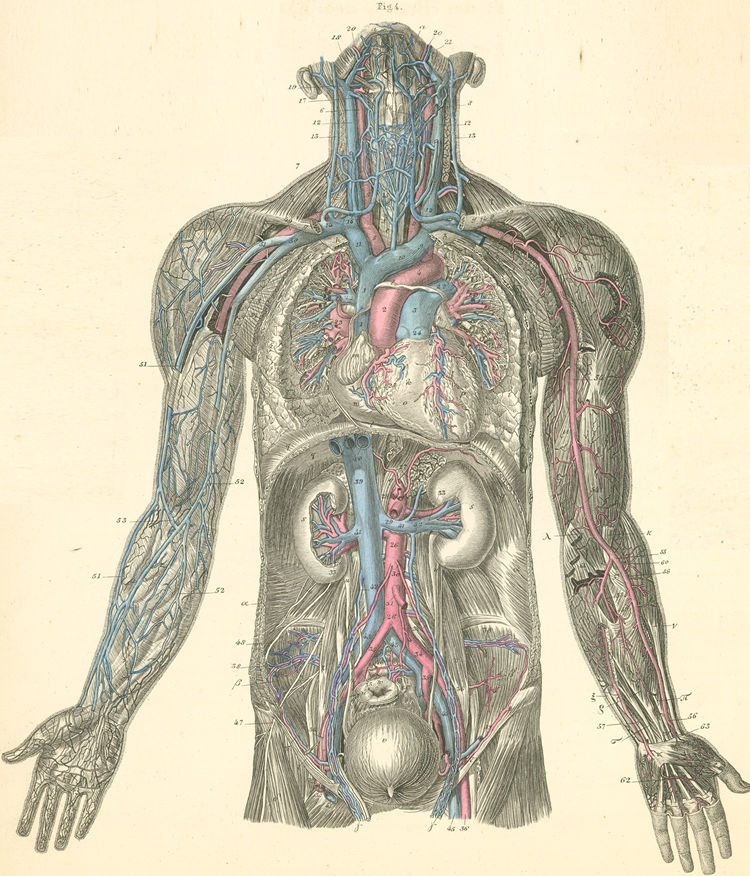
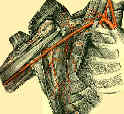
- right subclavian artery originates from innominate artery & passes into neck behind the right SC joint;
- left subclavian artery comes off aortic arch and enters neck behind left sternoclavicular joint;
- as it traverses the base of the neck, it lies between the anterior scalene and the scalene medius muscle;
- subclavian artery is divided into three parts by its relation to scalenus anticus muscle;
- at lateral border of first rib the subclavian artery continues as axillary artery;
- frxs of first rib or clavicle may cause injury to subclavian vessel, but this is rare;
- assoc neurological injuries frequently cause permanent disability;
- when neurologic deficit is caused by compression of brachial plexus by hematoma rather than by direct injury, early evacuation of hematoma may result in significant functional improvement;
- there are a few small series of patients with subclavian injuries w/ neurologic deficits:
- prompt exploratory surgery even in absence of distal ischemia, w/ goal of relieving compression on brachial plexus by hematoma;
- pts will improve if there is not direct injury to brachial plexus;
- ligation of the subclavian artery is usually well tolerated because of execellent collateral circulation around the shoulder girdle;
- Subclavian Artery Aneurysms:
- usually do to atherosclerosis, but may be due to trauma;
- if thrombosis is present, there may be emboli to hands;
- these may be either intrathoracic or supraclavicular (pulsating mass)
- usually is seen on the right side;
- most of these aneurysms contain mural thrombi
An Experience with Upper-Extremity Vascular Trauma.
Year Book: Management of Arm Arterial Injuries.