- See: Hand Tumors
- Discussion: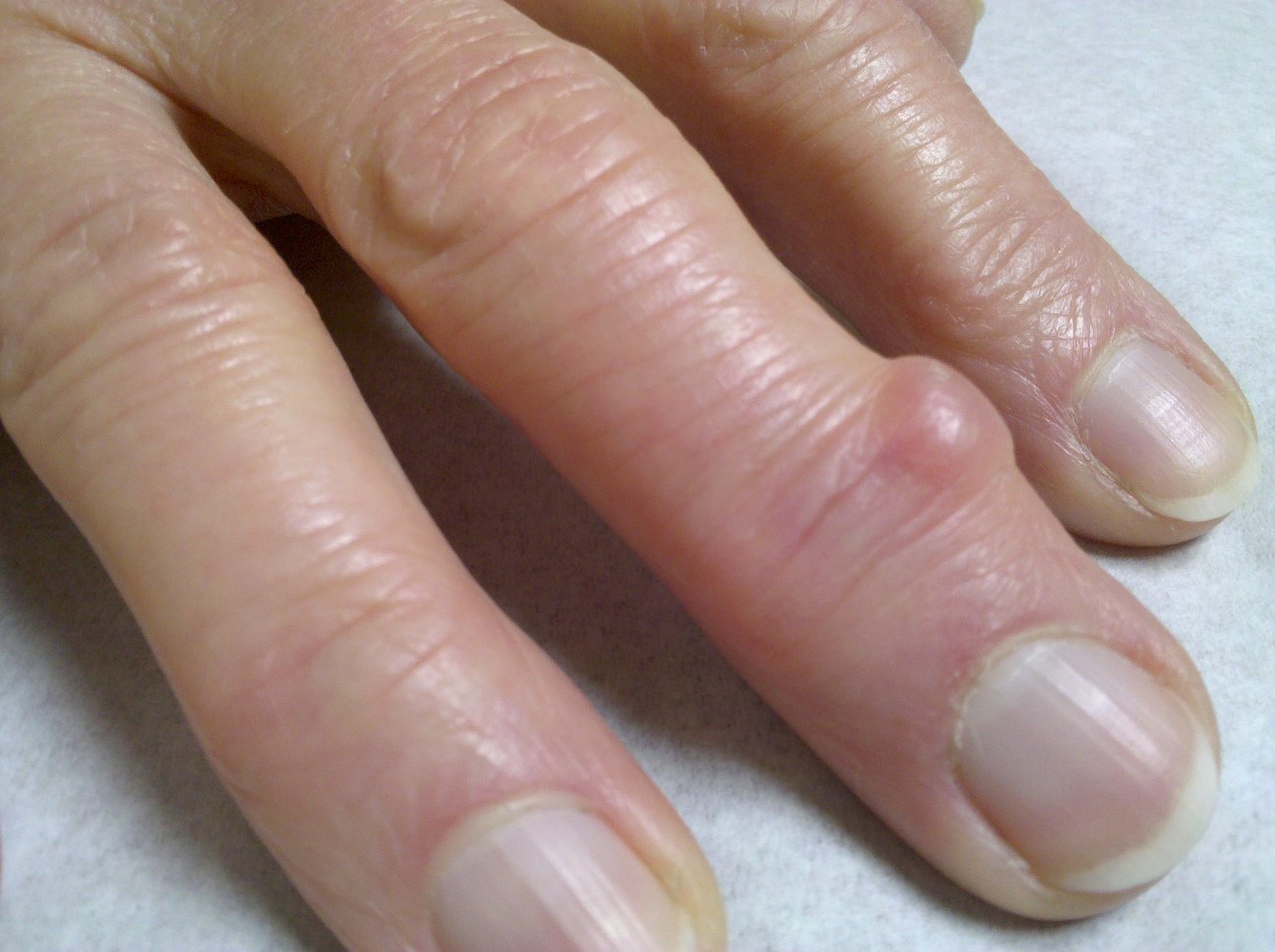
- cystic lesion (actually a ganglion) over dorsum of finger near DIP & fingernail;
- it is associated w/ degenerative lesions and spur formation (Heberden's nodes) over DIP joint;
- ganglion may or may not be connected to DIP joint by a synovial stalk;
- there may be associated with grooving of fingernail distal to the cyst;
- the nodule is usually flesh colored and is compressible;
- definitative dx may be made by transillumination or aspiration of synovial fluid;
- Exam:
- need to document ROM of DIP and whether nail deformities are present;
- Radiographs:
- need to look for associated osteophytosis and arthrosis of DIP joint;
- Non Operative Treatment Considerations:
- if mucous cyst ruptures & become infected, a septic joint may result;
- cysts which do not have a connecting stalk may be amenable to aspiration and injection of steroid;
- steroid injection:
- use 0.1-0.2 cc of triamcinolone 5mg/ml;
- Surgical Treatment Considerations:
- associated Heberdens's nodes, osteophytes should be removed at surgery;
- removal of the bony hump, which has attenuated the extensor tendon, may cause a mallet deformity;
- excision of the bony spur may initiate an arthritic flare up that can lead to a spontaneous joint fusion;
- ganglia of the distal joint area require complete excision, osteophyte resection, and skin reconstruction;
- of patients w/ preoperative nail bed deformities, only half can expect resolution of their nail bed deformity;
- Treatment: Removal of Osteophyte:
- if an osteophyte is present, it may be removed w/o disturbing the cyst;
- this minimizes the chances for nail matrix injury;
- this technique, however, may be associated w/ higher chance of recurrence;
- Technique of Cyst Removal:
- cysts is approached thru an L shaped incision and any attenuated skin is elliptically excised;
- cyst is mobilized, traced to the joint capsule, and excised w/ joint capsule;
- care is taken not to disturb the insertion of the extensore tendon or nail matrix;
- w/ the joint extended and the tendon dorsally retracted, the opposite side is explored and occult cysts are excised;
- Treatment: En Bloc Excision of Nail Fold:
- entire proximal nail fold (full thickness) is excised to a point just proximal to the cyst;
- insert the freer elevator under the nail fold upto the most proximal edge of the nail bed;
- this will protect the underlying nail, matrix, and extensor tendon;
- healing will occur by secondary intention over 6 weeks;
- Complications:
- residual loss of extension: 17%
- pyarthrosis of DIP joint: 2-3%
- nail deformities: 7%
- recurrence of deformity 3%
Outcome of surgically treated mucous cysts of the hand.
Complications Following Mucous Cyst Excision.
Finger Nail Deformities Secondary to Ganglions of the DIP Joint (Mucous Cysts).
Treatment of fingernail deformities secondary to ganglions of the distal phalangeal joint.

