- See:
- Soft Tissue Menu
- Desmoplastic fibroma
- Fibromatosis
- Discussion:
- solitary, beinign fibrous tumor of sof tissue;
- it may occur at any age;
- lesions arise as a slowly enlarging soft tissue mass;
- palmer and planter aspects of the hands and feet are common sites of involvement;
- lesion begins as active stage 2 lesion but then typically becomes latent;
- treatment:
- nonoperative treatment should always be tried and exhausted before considerations are made for excision;
- small lesions are especially amenable to orthotic treatment (insole is cut out over the lesion);
- excision, when, necessary, must be wide inorder to avoid recurrance (which is common);
- Juvenile Aponeurotic Fibroma:
- age under 20 years;
- localized to the hand and wrist more than 50% of the time;
- usually painless
- spotty calcification
- always benign but may be confused with calcification;
- treatment:
- excision:
- high recurrance rate;
- Fibroma of Tendon Sheath:
- attached to the tendon sheath or nearby structures such as lumbrical;
- one of the more common fibrous tumors;
- ages 20-50 yrs;
- may be found on the palmar surfaces of the hand;
- clinical diff dx: GCT of tendon sheath;
- treatment
- marginal excision, (recurrances have been reported)
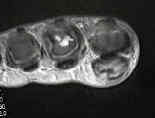
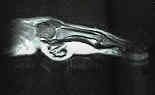
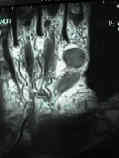
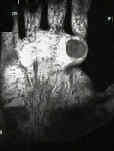
- Dermatofibroma:
- not true fibroma, it eneters into differential diagnosis of these firm nodular lesions;
- benign fibrohistiocytic tumors of dermatofibroma is a common mass involving the skin of many parts of the body;
- Nodular fasciitis:
- painful pseudosarcomatous, self-limiting reactive process composed of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts;
- seen in adults who are 20 to 40 years of age;
- immature-appearing fibroblasts that bear a close resemblance to the fibroblasts found in granulation tissue;
- fibroblasts are arranged in short, irregular bundles and fascicles and are adjacent to collagen and reticulin

