Discussion
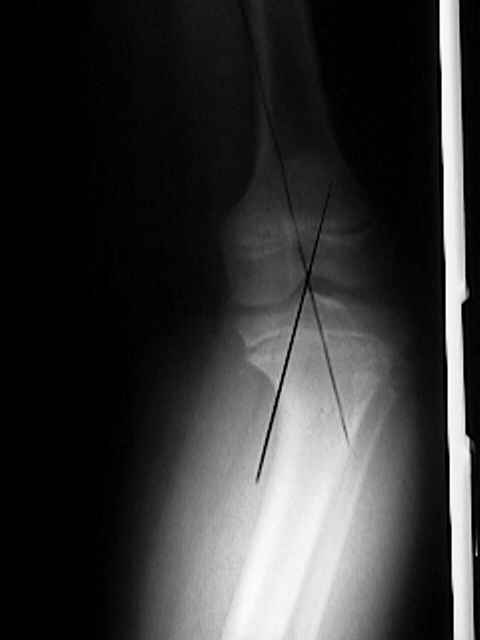
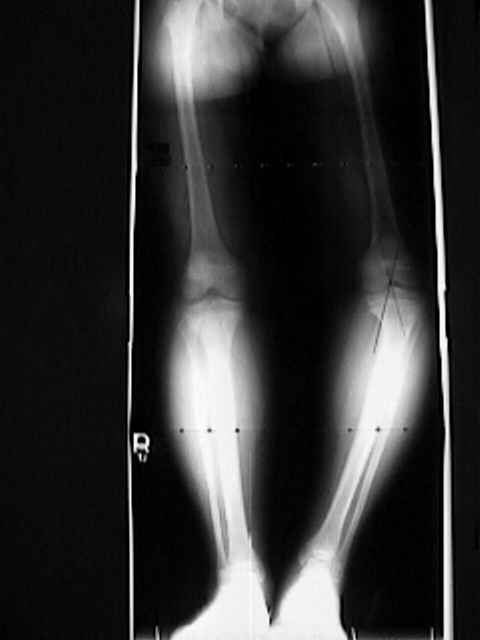
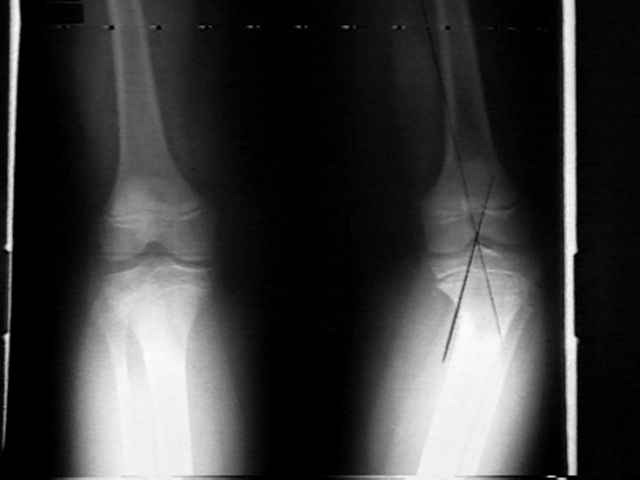
- adolescent tibia vara (Blount's disease), results from disordered growth of proximal medial physis & metaphysis;
- localized varus deformity, often accompanied by medial tibial torsion;
- caused by osteochondrosis resulting from mechanical stress converting physiologic bowlegs to tibia vara;
- risk factors: common in blacks & obese children;
- adolescent Blount's is less severe and predominately unilateral;
Treatment
- high tibial osteotomy:
- also consider need for valgus femoral osteotomy;
- Treatment of adolescent tibia vara by asymmetrical physeal distraction.
- Adolescent tibia vara: alternatives for operative treatment.
- Blount's disease after skeletal maturity.
- Comprehensive Treatment of Late-Onset Tibia Vara
- Outcome of Hemiepiphyseal Stapling for Late-Onset Tibia Vara.
- Results of Screw Epiphysiodesis for the Treatment of Limb Length Discrepancy and Angular Deformity.
- Treatment of Adolescent Tibia Vara with Hemiepiphysiodesis: Risk Factors for Failure