- Discussion:
- characterized by increased numbers of mast cells in vicera, principally liver, spleen, GI tract, and lymph nodes;
- skin may show numerous hyperpigmented macules that reflect dermal mast cell accumulation;
- symptoms of systemic mastocytosis are largely attributable to release of mediator substances from mast cells and include generalized puritis, uticaria, flushing, epsidotic hypotension, peptic ulcer, and syncope;
- skeletal manifestations include bone pain, tenderness, and deformity due to fracture;
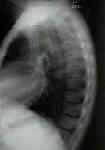
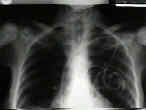
- Radiographs:
- diffuse poorly demarcated sclerotic and lucent areas that involve axial skeleton