- See:
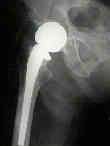
- Austin Moore Prosthesis:
- only true calcar support prosthesis is the old Moore implant, whose stem was too small to provide canal fill in most cases;
- designed for patients w/ 1/2 to 3/4 inches of remaining femoral neck above the lesser trochanter;
- collar of Austin Moore prosthesis is more transverse than that of Thompson prosthesis, fact that increases ability of the neck to
receive the compression stresses inserted on to it;
- Moore initially desinged his prosthesis with fenestrations in the stem in an effort to induce "self locking" and bony ingrowth;
- Moore prosthesis was designed with a transverse neck and is better suited for transverse frxs with adequate femoral neck remaining
to serve as a buttress;
- modularity is limited w/ this system, and the surgeon generally strives to obtain the best femoral head fit possible, which determines the
femoral stem size;
- it is possible that in cases of a "stove pipe femur" (w/ no taper), the ATM head will fit well, but the stem will be loose;
- in this situation, it may be preferable to abort to a cemented stem;
- note: never cement an AT Moore prosthesis, since it will be impossible to remove w/o severely damaging the femur;
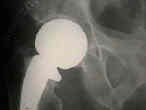
- Thompson Prosthesis:
- designed for pts w/ limited femoral neck above the lesser trochanter;
- designed in 1954, for use as a salvage prosthesis for femoral neck fractures, nonunions, in femoral neck fractures with a shortened
femoral neck (due to bony resorption);
- more vertical angle of the collar on the Thompson prosthesis tends to allow sinking of the prosthesis into the medullary cavity;
- this prosthesis may be cemented;
- Thompson prosthesis has a more vertical neck angle and is better indicated for the patient with a low or distal neck fracture