- Early Stages:
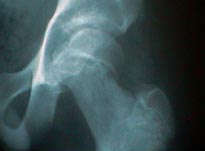
- widening of epiphyseal line (representing growth plate);

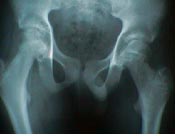
- AP View:
- normal hip shows epiphysis of femoral head projecting above & lateral to the superior border of the femoral neck;
- affected hip shows widening and irregularity of growth plate;
- height of the femoral head above the growth plate appears shortened as compared to the contra-lateral side;
- Klein's Line:
- line drawn along superior border of femoral neck should cross atleast a portion of the femoral epiphysis;
- slip must be suspected if a straight line drawn up lateral surface of femoral neck does not touch the femoral head;

- Lateral View:
- AP view may not reveal initial slip, which explains need for a true lateral lateral which will detect a posteriorly directed slip;
- w/ an acute slip, a frog leg lateral may be contra-indicated since it can increase the slip;
- w/ a chronic slip (or w/ a child who has been walking), a frog leg lateral is acceptable;
- the most sensitive indicator of a mild slip is the loss of lateral overhang of the femoral epiphysis;
- Southwick Slip Angle:
- head-shaft angle of the affected side is subtracted from the head-shaft angle of the normal side;
- the normal head shaft angle is 12 deg;
- Classification:
- Grade I: displacement of epiphysis less than 30% of width of femoral neck;
- Grade II: slip between 30%-60%;
- Grade III: includes slips of greater than 60% the width of neck;
- Chondrolysis:
- is seen as a progressive irregularity of subcondral bone & rarefaction of both the acetabulum & femoral head;
- initial pre-treatment radiographs may show loss of cartilaginous space (as compared to the other side);
- Misc:
- example of a valgus SCFE