- See: Cervical Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Clinical Findings:
- loss of lumbar lordosis;
- back motion is limited;
- note that ability to lean forward has more to do with hip flexion than lumbar spine flexion;
- w/ forward flexion there should be a reversal of the normal lumbar lordosis;
- hip flexion contractures or cervicothoracic kyphosis is common;
- these conditions require correction;
- may have fixed cervical, thoracic, or lumbar hyperkyphosis;
- may cause marked functional limitations, primarily due to inability of affected patients to face forward;
- pts may have diminished chest expansion;
- Spine Frx in AS:
- progressive neural deterioration;
- loss of reduction
- epidural hematoma;
- neurologic deficit occuring at higher level than at frx site may indicate expanding hematoma which is more common in AS;
- non union;
- occult frx;
- progressive kyphosis;
- death in > 50% of cases;
- Radiographic Changes:
- symmetric, bilateral subchondral erosions of the sacroiliac joints;
- subchondral sclerosis then follows, first on the iliac side and then on both sides of the joints.
- disease first affects lumbar spine and then ascends to thoracic spine;
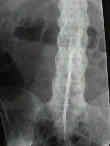
- vertebrae appear squared off on the lateral radiographs.
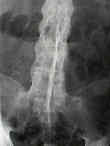
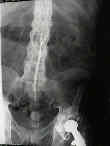
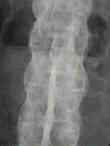
- longitudinal ligaments & annulus ossify, creating marginal syndesmophytes;
- spine takes on bamboo appearance from the sacrum to the occiput;
- SI joint obliteration & marginal syndesmophytes allow radiographic differentiation from DHIS;
- in Reiter's syndrome and Psoriatic Arthritis, beaklike nonmarginal syndesmophytes may be seen;
- fascet joint are simultaneously obliterated;
- Treatment:
- C-spine may be corrected by C7-T1 osteotomy & fusion w/ local anesth;
- complications of osteotomies include nonunion, loss of correction, & neurologic and aortic injury;
- extension osteotomy and fusion of the lumbar spine with compression instrumentation can successfully balance the head over the sacrum
Thoracolumbar fractures in ankylosing spondylitis. High-risk injuries.
The pathogenesis of extensive discovertebral destruction in ankylosing spondylitis.
Secure fixation of lumbar osteotomy. Surgical experience with 50 patients.