- Percutaneous Screw Placement:
- anterior column screws can be placed either antegrade (from cephalad to caudad) or retrograde (vice versa);
- implant: 7.3 or 8.0 mm cannulated screws;
- C-arm is placed perpendicular to the superior pubic ramus;
- inlet iliac view: helps to avoid guide wire penetration of the inner cortex of the superior ramus;
- outlet-obturator oblique view: helps to avoid guide wire penetration of the hip joint;
- antegrade insertion:
- used when the patient is in the lateral or supine position;
- starting point is 4-5 cm back from the ASIS;
- guide pin is driven down into the superior ramus using the inlet-iliac oblique (to ensure that the guide wire does not penetrate the
inner pubic ramus cortex) and the inlet-obturator oblique view ( to ensure that the guide pin does not penetrate into the hip);
- retrograde insertion:
- only used when the patient is in the supine position;
- difficult insertion when the patient is obese;
- use a 3 cm mini Pfannenstiel incision;
- guide pin is directed into the affected side pubic tubercle;
- guide pin is directed to a point posterior and inferior to the ASIS;
- guide pin is directed up into the superior ramus using the inlet-iliac oblique (to ensure that the guide wire does not penetrate the inner
pubic ramus cortex) and the inlet-obturator oblique view ( to ensure that the guide pin does not penetrate into the hip)
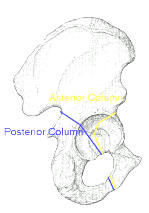
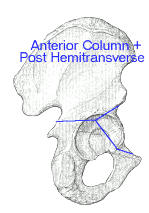
Anterior column fractures of the acetabulum.
Anatomic considerations of plate-screw fixation of the anterior column of the acetabulum.
Percutaneous fixation of the columns of the acetabulum: a new technique.
Percutaneous fixation of anterior column acetabular fractures--first experience
Axial view of acetabular anterior column: a new X-ray projection of percutaneous screw placement